CDISC standards in clinical research

The Clinical Data Interchange Standards Consortium (CDISC) is dedicated to the improvement of medical research through data standardization. CDISC has produced a suite of standards that should be used to standardize content from planning and data collection through to data analysis and reporting.
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) now requires studies to be submitted in this standardized format. This enables regulatory reviewers to evaluate and process clinical trials more effectively.
Implementing CDISC standards also has a number of benefits for the submitter, including:
- quicker design, build, and submission
- full traceability throughout the research process
- increased data quality
- reduction of costs
- streamlined processes
In this blog, we provide an overview of the CDISC standards used in clinical research.
Two groups of CDISC standards
CDISC standards can be grouped into two areas:
- Content standards
- Data exchange standards
1. Content standards
The content standards define what objects are allowed. For example, an Adverse Events dataset and the variables it contains.
Content standards fall under these four stages of the research process:
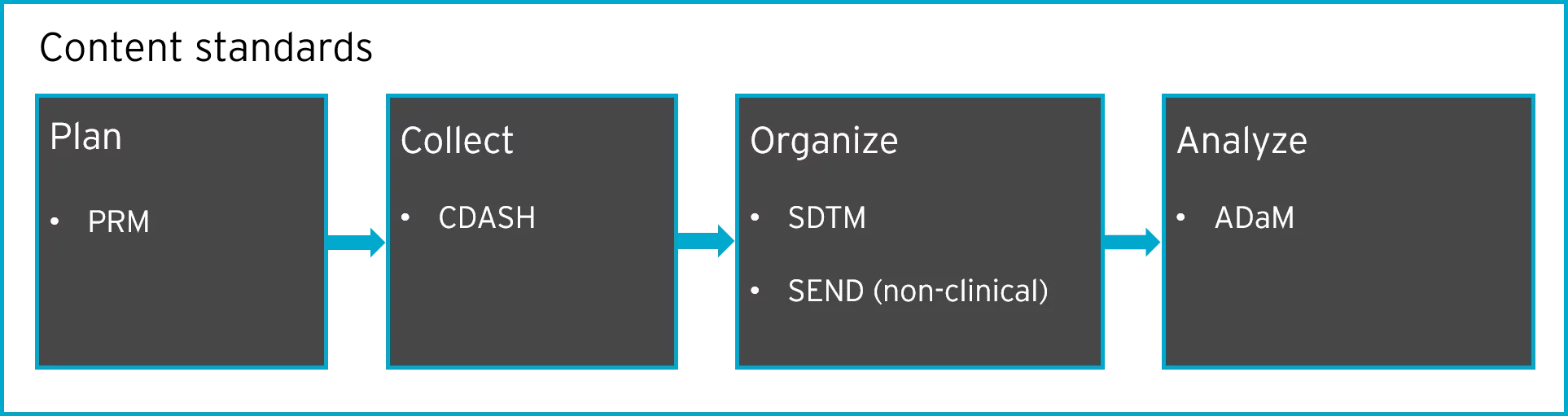
Protocol Representation Model (PRM)
PRM is the first stage in the clinical trial planning process. It’s a conceptual model that identifies items in the protocol and organizes them into a machine-readable structure.
PRM is not a deliverable and isn’t as commonly used as other CDISC standards such as SDTM and ADaM.
Clinical Data Acquisition Standards Harmonization (CDASH)
CDASH defines the best way to structure CRFs to gather all the relevant data needed for commonly used domains.
CDASH standards help to improve the quality of data, reduce queries, and make it easier to do the SDTM mappings required for regulatory submission.
Study Data Tabulation Model (SDTM)
SDTM was developed to organize data collected in clinical trials. SDTM gives a clear description of the structure, attributes, and content of each dataset, as well as the variables submitted as part of a clinical trial. SDTM metadata is submitted to regulators using the Define-XML data exchange standard.
To find out more, download our free guide to STDM mapping.
Standard for Exchange of Non-Clinical Data (SEND)
SEND standardizes the exchange of non-clinical data between systems in a consistent format. SEND metadata is submitted to regulators using the Define-XML data exchange standard. It’s an implementation of the SDTM standard that’s used for animal studies. In other words, data that is collected for animal studies can differ from data that is collected for humans, and the SEND standard attempts to bridge this gap.
The Analysis Dataset Model (ADaM)
The ADaM standard ties in closely with SDTM; ADaM datasets must always be derived from SDTM datasets. While SDTM is for collected data, ADaM is for presenting analysis data. ADaM metadata is submitted to regulators using the Define-XML data exchange standard, and the related Analysis Results Metadata standard.
Find out 3 things you should know about ADaM standards.
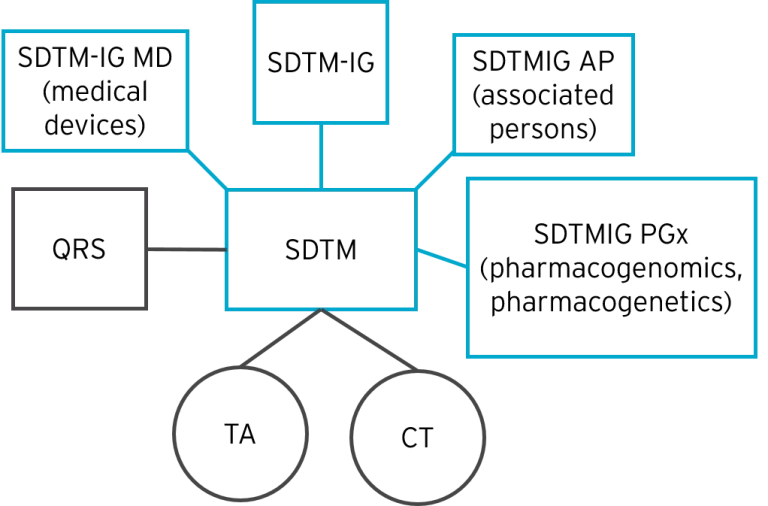
The different types of CDISC ADaM-related content that contribute to a final ADaM submission include:
- Questions, Ratings and Scales (QRS): QRS instruments are questions, tasks, or assessments for qualitative and quantitative assessment for clinical trials.
- Controlled Terminology (CT): A set of terminology standards published by CDISC and the National Cancer Institute (NCI) in partnership. These are used along with content standards like SDTM to help ensure that the content of the data is coherent and consistent. Read about using NCI controlled terminology for standardizing data.
- Therapeutic Area Standards (TA): These standards serve to represent data for specific therapeutic areas such as asthma, diabetes, multiple sclerosis, and more. Therapeutic Area User Guides(TAUGs) are implementation guides for each specific area. The CDISC foundational standards define in general how each different type of data should be submitted, TAUGs provide more specific information about how to interpret the foundational standards within a particular therapeutic area.
2. Data exchange standards
Data exchange standards are ways of representing metadata and data in a standardized way in order to make it easier to exchange data between different parties.
Data exchange standards described in this article include those in the diagram below:

ODM-XML
The CDISC Operational Data Model (ODM) is an XML-based model for standardizing the transfer of metadata and associated data for clinical trials. It can be used for defining the data collected in a trial, such as CRFs and patient diaries, to provide an upfront specification for the trial. This can then be used to help automate the build of the data collection systems or for transferring the data itself once collected.
The latest version is ODM-XML v1.3.2.
Dataset-XML
Dataset-XML supports the exchange of tabular data using ODM based XML technologies. It allows communication of study datasets for regulatory submissions.
Define-XML
Define-XML is a data model that allows a standardized description of tabular dataset structures, helping to drive process efficiencies throughout the clinical lifecycle. It describes the structure and content of data collected or submitted during the clinical trial process. This includes system-specific dataset structures that are exported from an EDC system and standardized CDISC domains such as SDTM.
It’s an extension of the CDISC ODM standard and is a key requirement for describing datasets that are to be electronically submitted to the FDA and PDMA.
Define-XML 2.1 is the current version of the standard.
Analysis Results Metadata (ARM)
CDISC standardized the description of ARM for describing tables, listings, and figures. This references the data in standardized ADaM datasets, making it easier to re-use analysis results metadata across different studies.
Laboratory Data Model (LAB)
LAB was established to standardize the transfer of data between clinical laboratories and sponsor companies. The CDISC LAB model is widely used in pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies today.
It was developed because of the many variations between data acquired in laboratories, such as lab test names and units. Using the LAB model, laboratory data is standardized allowing seamless transfer between laboratories and CROs, which saves time and costs.
Get in touch
At Formedix, we’re strong advocates for the use of CDISC data standards in clinical and non-clinical research. In fact, we’re on the CDISC XML technical team and were involved in creating the CDISC ODM and Define models.
If you have any questions about the standards discussed in this article, get in touch to speak to an expert.












