How clinical trial software can be used to optimize clinical trials

Clinical trial software facilitates clinical trials from conception to finish. For example protocol management, CRF design, metadata management, and the collection, analysis, and submission of compliant clinical study data to regulatory authorities. The aim is to get quality clinical products to the market faster.
Traditionally spreadsheets have been used to record and manage all the various aspects of clinical trials. That means there’s a high risk of errors, not getting vital data, and for there to be bottlenecks in the process. So efficiency, compliance, and patient care have been compromised.
The industry is now recognizing that to stay ahead of competitors, technological cloud-based clinical trial software solutions are key for faster, more efficient clinical trials. And the FDA has been encouraging the use of cloud-based solutions to streamline the clinical trial process.
Types of clinical trial software
Clinical trial software encompasses many different types of software for different stages in the clinical trial process. Some of them include:
- Clinical Trial Management Systems (CTMS)
- Electronic Data Capture system (EDC)
- Integrated clinical study automation software
What is a CTMS?
A CTMS is an integrated cloud-based software platform that’s used for the end-to-end management of clinical trials. They help companies improve the quality of their clinical products, reduce the time it takes to get a product to market and ensure compliance with industry standards and regulations. They’re used to plan, track, and analyze clinical trials. And to find and manage participating patients, track their involvement in clinical trials, and manage finances.
What is an EDC system?
It’s an electronic system that lets users gather patient data during clinical trials. They typically have a user interface for users to enter data into electronic forms. Validation to check forms have been filled in accurately. And a reporting tool to let users analyze the data collected.
Modern EDCs let you target specific patient profiles or study phases. Features can include cloud data storage, role-based permissions, CRF designers, clinical data analytics, interactive dashboards, and electronic health record integration.
The main benefits of using an EDC system are that they increase data accuracy, speed up the data collection process, and reduce costs over the lifetime of a clinical trial.
What is meant by integrated clinical study automation software?
Clinical study automation software is an integrated cloud-based software that specializes in specific parts of a clinical trial. These types of systems vary and can cover areas such as CRF designers, metadata management, standards governance, data warehousing, statistical computing, and submission to regulatory authorities.
An example of this type of software is the Formedix clinical trial automation platform and clinical metadata repository. Our automated processes are streamlined for CRF design, data collection, tabulation, analysis, and submission. With CDISC compliance and validation built-in.
What is a clinical metadata repository?
It’s a web-based, centralized, governance platform that lets organizations store, manage, and reuse all of their metadata.
Metadata can be stored in various stages of development. It can be updated, approved, and kept as organizational standards.
The key drivers are:
- Regulatory compliance.
- High data quality.
- Process efficiency.
- Reuse.
Using a clinical metadata repository (MDR) results in saved time, a reduced need for resources, and the ability to get quality products to the market quicker.
What are the main features?
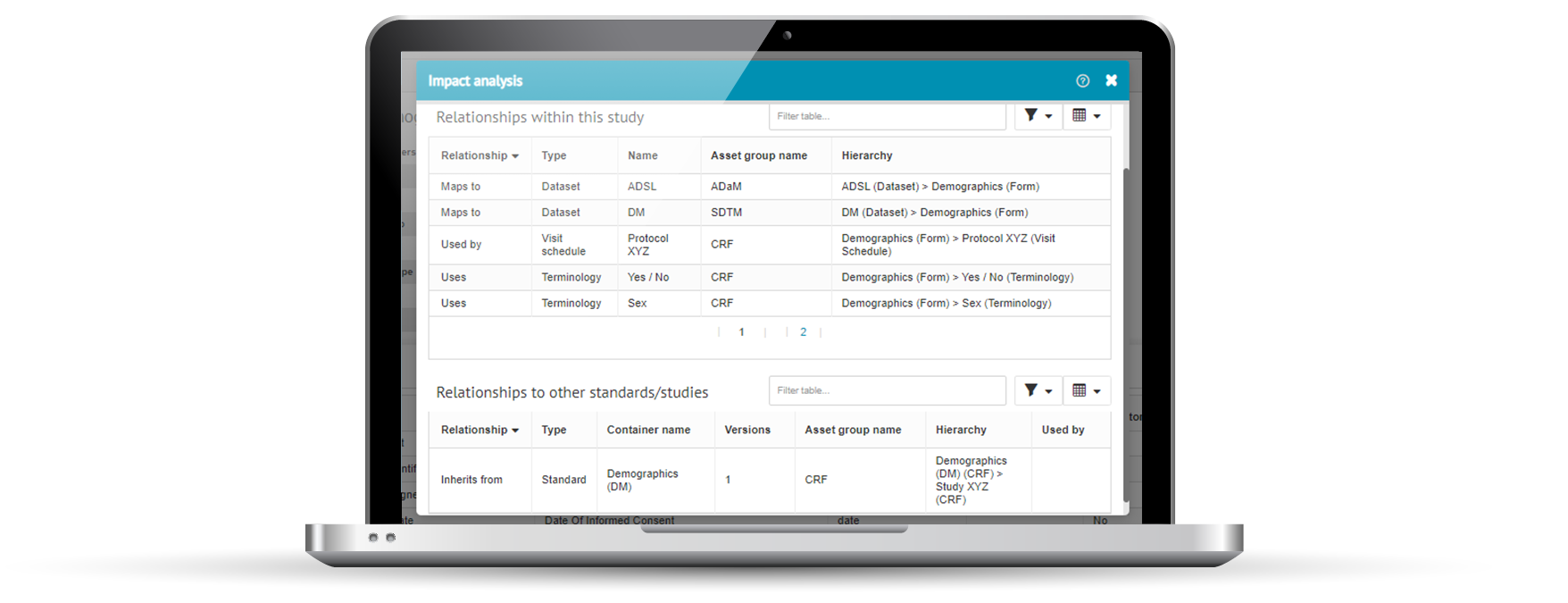
Impact analysis
Impact analysis is a key objective of clinical metadata repositories and should be built-in. It lets you see what upstream and downstream metadata and processes are affected if a particular change is made. Before you make that change.
Impact analysis puts you in a much better place to make informed decisions on whether a proposed change is worth making, or not.
Change management
There should be a way for team members to request changes to existing metadata content. It must be possible to edit, add, and retire metadata content. The change management process should record what the change is, why it’s been requested, who made the change, who requested the change, when the change was requested, and when the change was made. These changes should go through a well thought out governance process. See the example below.
Governance
Governance refers to the process that must be adhered to for any change to existing metadata content and organizational standards. Or for the creation of new metadata content. A governance process, or workflow, must be built in to make sure that changes are managed and dealt with effectively in a way that suits an organization’s needs.
Versioning
A quality clinical metadata repository should allow versioning of internal standards across the organization. It should let you update and improve both study level standards and organizational standards. For example, you might want to have various versions of the same CRF for different purposes. And changes to a version of a CRF will have an impact on SDTM mappings and TLFs (tables, listings, and figures).
Built-in compliance and validation
Compliance and validation ensure that a clinical study meets the expectations of regulatory authorities. It should be built in from the start of a study, through to submission. So each part of the study should be tested against validation rules to make sure it stays compliant.
Automated processes and clinical MDRs
Automation simplifies processes for clinical studies, from study setup through to submission. It helps to speed studies up and to reduce human error by removing manual processes. It makes it easier for companies to comply with regulatory standards and guidelines set out by regulatory authorities.
Here are the main benefits for organizations:
- Get clinical trials done faster.
- Improved metadata quality and consistency.
- Analyze data more quickly and effectively.
- Reduce overall costs.
Automation improves clinical trial efficiency and means your submission will be of better quality. Fewer resources are needed, and costs are saved.












