Genfit announces data from algorithm-based NASH test
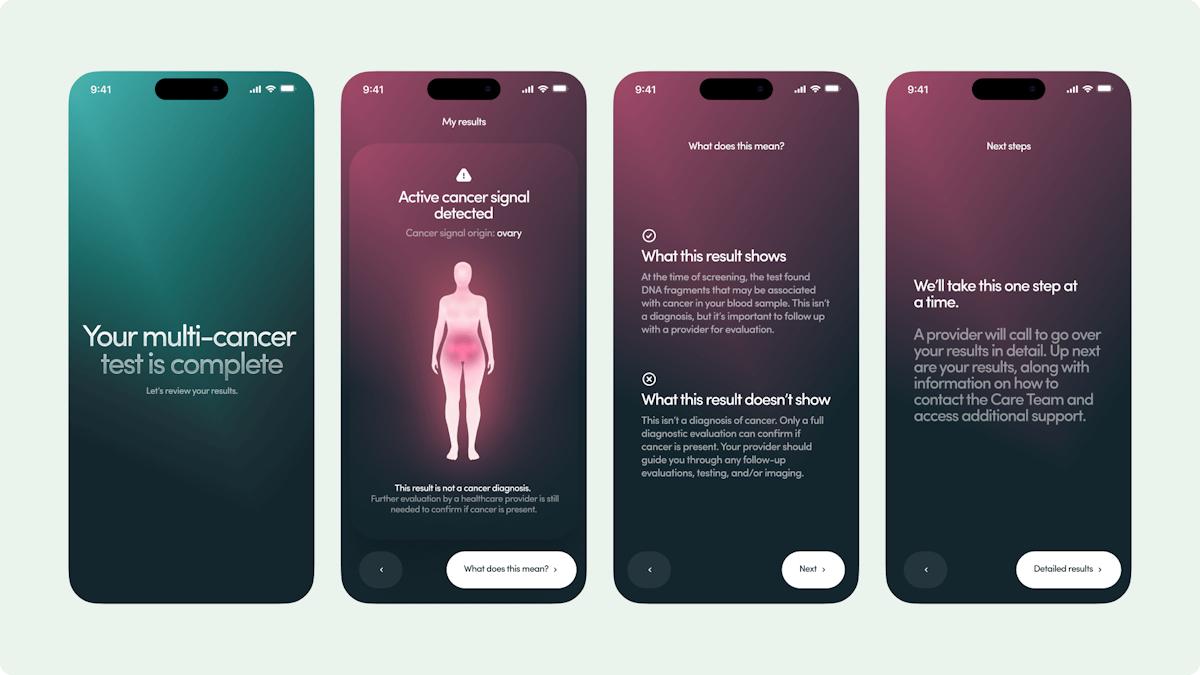
The pharma company Genfit has announced supportive data from a study involving a non-invasive algorithm driven blood test for the fatty liver disease known as NASH, a potential replacement for liver biopsy, the standard method of diagnosis.
Genfit announced results from a study demonstrating NIS4, an innovative non-invasive diagnostic blood test designed to diagnose nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), outperformed other non-invasive diagnostics in identifying the disease in people with type 2 diabetes.
Data presented at AASLD The Liver Meeting 2019 in Boston explores how type 2 diabetes is a risk-factor for NASH and liver fibrosis, and also compares the diagnostic performance of NIS4 versus other non-invasive blood marker-based scores in a population of patients with type 2 diabetes.
NIS4 is based on a panel of four biomarkers measured using an algorithm to detect the disease, which is predicted to produce a new generation of blockbusters for pharma as there are no currently approved treatments.
A first cohort of 820 patients assessed the influence of type 2 diabetes status and anti-diabetic treatment on the prevalence of biomarkers active NASH (NAS>4) and fibrosis (F>2), while a second cohort of 275 patients assessed the diagnostic performance of a biomarker called NIS4 in patients with type 2 diabetes.
The data show that of the patients in Cohort 1, the presence of type 2 diabetes is associated with increased prevalence of NAS>4 and significant fibrosis, who are at risk of progression to serious liver outcomes.
The probability of having NAS>4 with F>2 increases with the number of additional anti-diabetic therapies taken by patients to control their glycaemia, irrespective of the antidiabetic drug classes used, whether insulin or non-insulin drugs.
Genfit said the data show the need for active surveillance of liver injury in patients with type 2 diabetes, in order to identify those at need of intervention to prevent evolution to clinically relevant hepatic outcomes.
But crucially the data from cohort 2 also show that NIS4 significantly outperformed existing non-invasive diagnostic tests in accurately identifying active NASH and significant fibrosis in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Genfit said findings showed NIS4 can demonstrate good diagnostic performance and accurately identify NASH and significant fibrosis in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Stephen Harrison, study author and Medical Director of Pinnacle Clinical Research, said: “While liver biopsy is the current clinical reference standard for diagnosis, it is a costly, invasive procedure that can cause pain and discomfort for patients, and can even have serious, life-threatening complications.
“Currently there are no minimally-invasive tests approved specifically for NASH, which is expected to soon be the primary cause of liver transplant.”
Intercept Pharmaceuticals is leading the race to develop a drug for NASH, with its obeticholic acid under review with the FDA and a filing is due with European regulators in the coming weeks.