Streamlining JCA response with GenAI

The Joint Clinical Assessment (JCA) framework took effect on 12th January 2025, and its impact is top of mind among pharma innovators today.
The policy was the buzz of the International Society for Health Economics and Outcomes Research (ISPOR) annual European meeting in late November 2024, where no fewer than 19 sessions covered JCA considerations, with countless vendors offering guidance. Artificial intelligence (AI) and generative AI (GenAI) featured prominently in each session, in one way or another, as a potential tool to help expedite submissions, and even elevate their quality.
So, why is the JCA creating such a stir?
To recap, the JCA framework is intended to expedite cooperation on health policy among EU member states. Proposed by the Health Technology Assessment (HTA) Coordination Group (HTACG) in 2020, it requires life sciences companies to harmonise clinical evidence across the 27 EU countries and make a clinical submission to the European Commission. The JCA submission requires clinical and comparative effectiveness data and, once submitted, will be reviewed by the HTAs within each member state.
The first wave of JCA implementations affect new oncology and advanced therapy medicinal products. The very tight JCA timeline typically gives life sciences companies just 90 days from receiving confirmation of their PICOs (Population, Intervention, Comparator, Outcomes) to submitting their JCA dossier. The JCA essentially creates an additional – aggressive – regulatory deadline, with an increased burden for content and data aggregation, synthesis, analysis, summarisation, translation, and scrutiny.
What can help life sciences innovators strive to meet this new regulatory hurdle?
GenAI can help with JCA submissions tremendously. With seven years of experience in which numerous large pharma companies and CROs have deployed AI solutions in production, GenAI has demonstrated it can facilitate tedious, time-consuming processes in need of thoughtful, highly skilled oversight. These processes each involve compilation, synthesis, analysis, summarisation, and translation – exactly what is required to successfully submit a JCA dossier in the limited timeframe available.
Where specifically can GenAI help in the JCA submission process?
Across the major steps of the JCA submission timeline (Figure 1), GenAI can deliver significant time-savings in four key areas – ultimately enabling more timely, higher-quality submissions.
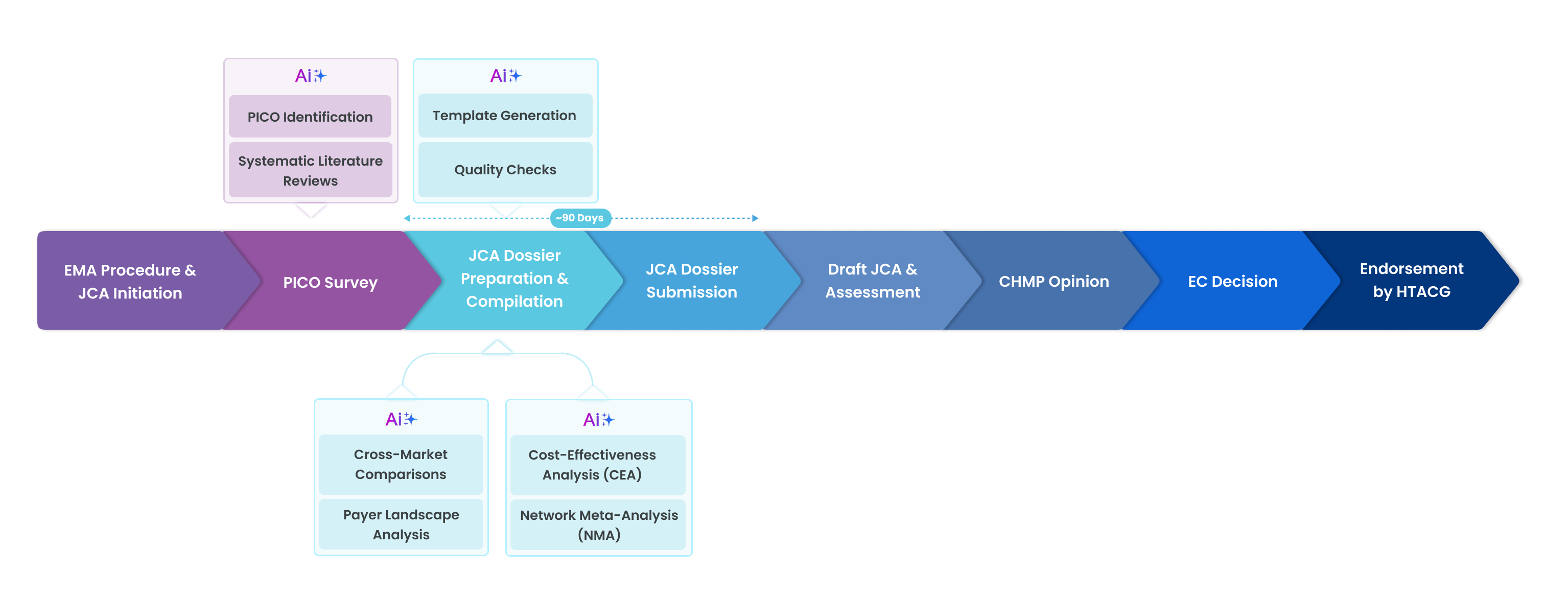
Figure 1. JCA process and opportunities for GenAI-powered acceleration.
Compiling and synthesising
A significant component of JCA involves the synthesis of large amounts of medical literature and clinical trial data. GenAI-enablement expedites this synthesis, automating it from weeks of research down to hours of GenAI-assisted synthesis. For activities like systematic literature review (SLR) – a necessary component of JCA submissions – GenAI-enabled SLR platforms can automate the manual research process and accelerate identifying, assessing, and synthesising relevant studies and information required for JCA submissions, cutting down the time it takes to find supporting evidence. Published data indicates that pharma companies using novel GenAI-enabled platforms have completed their SLRs 40% faster while maintaining content quality.
In addition, GenAI-enabled meta-analysis allows for the comparison of clinical outcomes across multiple studies, essential for JCA assessment requirements. In conducting this clinical evidence mapping, GenAI can identify and extract relevant studies from massive datasets to align with PICO criteria. GenAI can also be used for real-time meta-analyses to compare treatment effectiveness across different patient groups.
Generating HTA reports and automating submissions
GenAI’s content generation capabilities can streamline the creation of structured regulatory reports for JCA submissions mandated by the HTA, reducing manual effort and minimising errors. Data extraction and formatting tools can automate HTA templates, ensuring compliance while alleviating workload burdens. Additionally, GenAI-powered language translation facilitates multi-country regulatory submissions by adapting documents for various EU markets.
Applying GenAI also enhances regulatory dossier summarisation by processing large volumes of clinical trial data and extracting key insights for JCA submissions. Natural language processing (NLP) aids in drafting JCA reports by compiling relevant clinical assessment information, reducing human effort and potential inaccuracies. Furthermore, GenAI accelerates comparative analysis by evaluating past JCA reports, identifying trends, and providing data-driven insights to support informed decision-making.
Analysing clinical and real-world data
Using GenAI for extraction from global value dossiers (GVDs) can facilitate the identification of key clinical data elements needed for JCA submissions – for example, safety and efficacy data. To enhance clinical trial information in JCA submissions, GenAI can analyse real-world data (RWD) from sources such as electronic health records (EHRs), patient registries, and wearables, enriching a therapy’s effectiveness and safety dataset. Some pharma companies monitor social media as well for RWD, to further enrich their datasets.
Leveraging RWD, large language models (LLMs) can predict long-term treatment outcomes, enabling the comparison of the potential efficacy for new therapies. GenAI-driven signal detection can analyse pharmacovigilance databases to identify and flag adverse events early, improving drug safety monitoring. Additionally, its patient stratification can support therapy evaluation by identifying specific subgroups within a population that would benefit most from a treatment.
Monitoring regulatory updates, and HTA alignment
By applying GenAI-powered monitoring of evolving EU regulations, life sciences professionals and key stakeholders can obtain a proactive alert to updates in JCA requirements. GenAI also can automate the mapping of clinical evidence to standardised JCA criteria, helping identify compliance gaps and ensuring regulatory alignment.
Additionally, using GenAI-driven document classification can streamline regulatory submissions, facilitating faster alignment with EU HTA requirements. GenAI-systems can also conduct regulatory compliance checks to assess whether health technology submissions meet EU HTA and EMA guidelines. Furthermore, automated timeline management capabilities enable GenAI-solutions to track submission deadlines and notify stakeholders of upcoming JCA milestones, ensuring timely compliance.
Toward faster, higher-quality JCA submissions
Life sciences leaders that apply GenAI to their JCA submissions gain an essential tool for navigating this regulatory hurdle. They can reduce the most labour-intensive aspects of JCA compliance, such as literature reviews and systematic analyses. They minimise manual effort, enabling researchers to focus on validation, and allow seamless aggregation of diverse data sources. They monitor updated regulatory needs, to help eliminate knowledge gaps and keep stakeholders informed of evolving JCA requirements.
Given the complexity of JCA tasks, GenAI stands out as a powerful enabler to meeting this additional, stringent regulation with more timely, higher-quality submissions. By driving automation and optimisation, GenAI empowers life sciences professionals to achieve their JCA compliance efficiently and effectively.
References:
i. “Joint Clinical Assessment for Medicinal Products,” European Commission’s Health Technology Act (HTA), as posted at https://health.ec.europa.eu/document/download/ced91156-ffe1-472d-85eb-aa6a91dd707e_en?filename=hta_htar_factsheet-jca_en.pdf.
About the author
 Gaugarin (“G”) Oliver is the founder and CEO of CapeStart, Inc., a professional services firm supporting the healthcare and life sciences industry.
Gaugarin (“G”) Oliver is the founder and CEO of CapeStart, Inc., a professional services firm supporting the healthcare and life sciences industry.












