Innovative sublingual medication for improved stroke care

Stroke poses a major threat to public health, and this threat is predicted to worsen in the years to come. Simcere is a company dedicated to creating novel therapeutic solutions to meet this urgent medical need.
Stroke remains a leading cause of disability and death worldwide, with the incidence rate continuing to rise due to ageing populations and an increase in associated risk factors. Annually, 15 million people suffer from stroke worldwide, and the rising incidence is predicted to lead to 10 million deaths per year by 2050. Despite advances in prevention and acute care, existing treatment options are still limited, especially due to the fact that the therapeutic window for successful intervention is particularly short.
The limitations of existing medical options and the growing economic burden underscore the urgent need for innovative therapies which can effectively treat stroke patients beyond the aforementioned therapeutic window, especially for acute ischemic strokes, which account for 70-87% of all stroke cases.
The mainstay of AIS management is endovascular reperfusion therapy aiming to restore blood flow to the ischemic regions of the brain and prevent stroke-related disability and mortality. The time-window for reperfusion therapy is the most crucial factor associated with the clinical outcomes; that is, the faster the drug delivery, the better the outcomes.
Although reperfusion therapy (thrombolysis or thrombectomy) remains the first treatment choice according to guidelines, ineffective (futile) reperfusion or reperfusion injury can be seen in a significant number of patients (~50%) undergoing reperfusion strategy. Due to the limited time window and accessibility of EVT (endovascular therapy), less than 20% of AIS patients are eligible for reperfusion therapy.
It is expected that neuroprotective drugs could benefit more patients outside the reperfusion treatment window. An ideal brain cytoprotective agent should act on multiple targets or have multiple mechanisms of action to address various pathological factors associated with ischemic stroke. Dr Felix Wang, Senior Vice President of Simcere Pharmaceutical Group Limited, spoke with pharmaphorum about the potential of brain cytoprotective agents to reduce ischemic brain injury, as well as the work Simcere has undertaken to develop the only innovative stroke drug approved in the last decade globally.
Creating a dual-targeting therapy
Sanbexin is a concentrated solution for injection composed of edaravone and dexborneol. Wang stated that it took over 13 years for the company to develop Sanbexin, which has been validated in a multi-centre, randomised, double-blind Phase 3 clinical trial in China. Brain cytoprotection against stroke can hardly be achieved by a single-target neuroprotective drug, given the complex pathophysiological mechanisms of stroke, Wang said. The satisfied clinical outcome of single-target brain cytoprotective agents is very difficult to achieve due to insufficient treatment efficacy.
The combination of the two active compounds that comprise Sanbexin was pursued after Simcere uncovered the anti-inflammatory activity of dexborneol in the brain, as well as BBB protection and GABAaR positive modulation, etc. In light of these findings, Simcere further developed this edaravone and dexboneol combination drug with multi-targeting MoAs to achieve the synergistic effects of antioxidant and anti-inflammatory in protecting brain cells from ischemic injury.
“This therapy exerts its efficacy through various pharmacological mechanisms synergistically, including the anti-inflammatory effect, free radical scavenging, reduction of blood-brain barrier disruption, and mitigation of excitotoxicity, thereby significantly reducing the cascade damages caused by brain ischemia-reperfusion,” Wang added.
Supported by the results of Phase 3 clinical trials, which showed that this combined medication was more effective than edaravone monotherapy, Sanbexin has been approved for marketing in China. The incidence of stroke in China ranks the highest globally and is the leading cause of death, highlighting the urgent need for new stroke therapies.
Drawing on the benefits of sublingual administration
Soon after successfully developing the intravenous injection of Sanbexin, Simcere began to work on the formulation of sublingual tablets of Sanbexin.
“Considering the limitation that intravenous injection can only be used in the hospital, we have developed the sublingual tablets since 2016, which are more convenient to administer and can achieve higher patient compliance, in parallel with the development of Sanbexin injection,” Wang explained.
The sublingual route of administration addresses one of the major challenges of stroke treatment: the treatment time window. Upon the onset of a stroke, irreversible damages to the brain occur, with millions of brain cells dying every minute, Wang stated. The later the access to treatment, the more severe the damage to the brain, which can lead to worse disability and prognostic implications.
When delivered by a sublingual route of administration, the tablets dissolve within seconds and are absorbed into the blood circulation and brain through the sublingual venous plexus. Another benefit is that the drug can be delivered to the brain while avoiding the first-pass metabolism, thus elevating the drug’s bioavailability.
Swallowing dysfunction, otherwise known as dysphagia, is also very common among stroke sufferers. According to reports, it is estimated that 30-65% of stroke patients are suffering from dysphagia. This condition might interfere with treatments with oral drugs. Unlike intravenous injections, sublingual tablets can also be used outside of the hospital setting, offering the potential of use at home to allow for immediate brain cytoprotection for stroke patients in emergencies.
According to Wang, Simcere is also investigating whether the injection and sublingual formulations can be combined as a sequential therapy, providing patients with more effective treatment and improved prognosis.
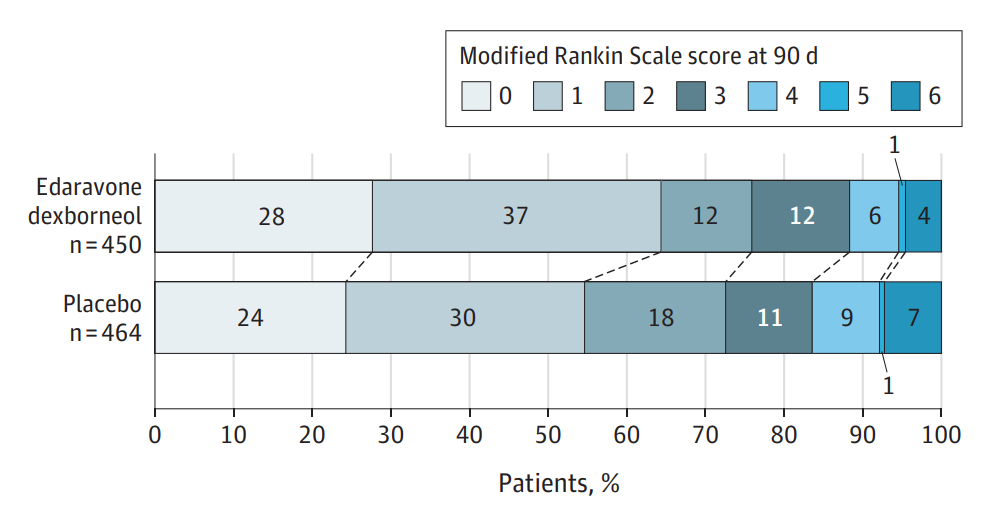
To support the international regulatory submissions, the company is carrying out several clinical trials on the efficacy of Sanbexin, both in sublingual and intravenous formulations. Simcere published the results of the Phase 3 study investigating the efficacy of sublingual edaravone and dexborneol used within 48 hours after an acute ischemic stroke.
Results from the trial showed that the proportion of subjects with modified Rankin Scale (mRS) scores of 0 or 1 (indicating no significant dysfunction) on day 90 was significantly higher in the treatment group compared to the placebo group. Overall, 64.4% of patients treated with the sublingual tablets (vs. 54.7% in the placebo group) had good functional outcomes. The safety profile of Sanbexin was similar to that of the placebo (89.8% vs. 90.1%, respectively).
Advancing the development of brain cytoprotection therapies
Due to the potential in the treatment of acute ischemic stroke, Sanbexin sublingual tablets have been granted the Breakthrough Therapy designation by US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), thus becoming the first innovative drug in the world with this designation for the treatment of AIS. In light of this designation, the development and review process for Sanbexin will be expedited, and enhanced communication will take place between Simcere and the FDA to provide constructive feedbacks and guidance throughout the R&D process, Wang said.
On 1 December, the Sanbexin sublingual tablets received approval from China’s National Medical Products Administration (NMPA). The marketing approval for the injection formulation of Sanbexin has already been granted in China in 2020, with over three million patients benefitting from access to the drug in the past four years.
Wang explained that Simcere is currently conducting an extensive clinical trial programme on Sanbexin for various stroke-related indications, including efforts to validate the efficacy of Sanbexin outside China. With this in mind, the company is preparing a global multi-centre Phase 3 clinical trial of Sanbexin sublingual tablets in the treatment of acute ischemic stroke.
The company is also advancing two Phase 2 clinical trials on Sanbexin, with one trial focusing on the application of Sanbexin injection in treating haemorrhagic stroke, and the other trial exploring the potential of sublingual tablets in treating post-stroke cognitive impairment.
Wang mentioned that this drug is expected to serve as an acute stroke management medication, which will be applicable to subacute and chronic phase treatments of cerebrovascular diseases, potentially reaching a broader patient population affected by acute and chronic cerebrovascular conditions.
For Simcere, multiple marketing approvals for Sanbexin in China and the Breakthrough Therapy designation granted by the FDA both mark the progress of the company since making the central nervous system one of its strategic focuses in 2004.
“The innovation of sublingual formulation is the result of continuous trial and error according to clinical needs. Brain cytoprotection is an area where innovation is not easy, and it is due to our endeavours and good fortune to be able to fill this gap.” Wang concluded.
About the Interviewee
 Dr Felix Wang is the Senior Vice President of Simcere Pharmaceuticals. He is responsible for the management of R&D systems, and the Collaborative Innovation division of Simcere. Dr Wang received a Master's degree in Microbiology and Biochemical Pharmacy and a Doctorate in Social and Administrative Pharmacy from China Pharmaceutical University. Dr Wang joined Simcere in 2007 and has extensive experience in regulatory registration and has led/participated in the R&D and marketing of multiple innovative drugs of the group. He currently serves as the Secretary-General of the Pharmaceutical Policy Professional Committee of the China Pharmaceutical Innovation and Research Development Association(PhIRDA).
Dr Felix Wang is the Senior Vice President of Simcere Pharmaceuticals. He is responsible for the management of R&D systems, and the Collaborative Innovation division of Simcere. Dr Wang received a Master's degree in Microbiology and Biochemical Pharmacy and a Doctorate in Social and Administrative Pharmacy from China Pharmaceutical University. Dr Wang joined Simcere in 2007 and has extensive experience in regulatory registration and has led/participated in the R&D and marketing of multiple innovative drugs of the group. He currently serves as the Secretary-General of the Pharmaceutical Policy Professional Committee of the China Pharmaceutical Innovation and Research Development Association(PhIRDA).
About Simcere Pharmaceutical

Simcere Pharmaceutical Group Limited (2096.HK) is a pharmaceutical company driven by innovative R&D. Being committed to “providing today’s patients with medicines of the future” across the following core therapeutic areas: neuroscience, anti-oncology, autoimmunity and anti-infection, Simcere has established strategic partnerships with multiple innovative companies and research institutions.
Simcere has established four R&D centers in Shanghai, Nanjing, Beijing and Boston. With a comprehensive R&D system, it has pipelines of nearly 60 new drug development projects. Up to date, Simcere has commercialized 8 innovative drugs on the China market.